Whole Body Bone Scan
Purpose:
Provides a comprehensive evaluation of the skeletal system to detect bone metastases, fractures, or other abnormalities
How It Works:
A radiotracer (typically Tc-99m MDP) is injected into the bloodstream, which then accumulates in areas with increased bone turnover.
Clinical Significance:
Ideal for screening and staging in patients with known or suspected metastatic cancer.
Helps monitor treatment response and detect early signs of recurrence.
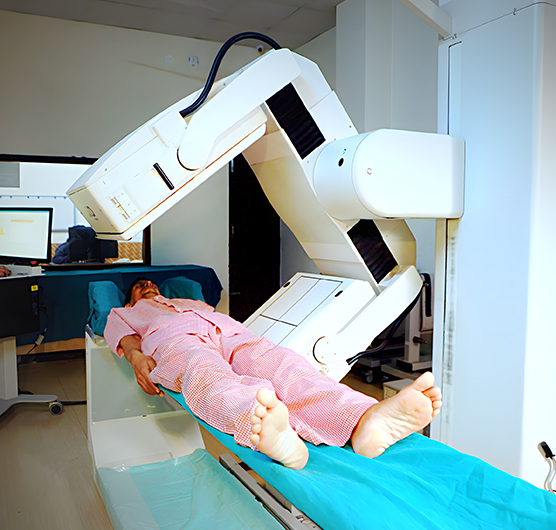
Gamma Camera Scan Services in Rohtak, Haryana
- .Thyroid Scan: Provides detailed imaging for the assessment of thyroid function and abnormalities.
- Parathyroid Scan: Assists in identifying parathyroid gland disorders and pinpointing gland location for potential surgical intervention.
- Iodine-131 Whole Body Scan: Primarily used for post-treatment evaluation in thyroid cancer patients, helping track residual or recurrent disease.
- Iodine-131 MIBG Scan:Effective in diagnosing and managing neuroendocrine tumors, visualizing areas of abnormal uptake.
- Bone Scan (MDP) Whole Body: Evaluates bone health, detecting fractures, infections, or metastatic bone disease with high sensitivity.
- Tc-99m Whole Body Scan: A comprehensive scan for detecting and evaluating various conditions in different body systems, offering a diagnostic overview. for 7 seconds
Thyroid Scan:
Utilizes radioactive tracers to assess thyroid function and morphology.
Parathyroid Scan:
Targets the parathyroid glands to detect abnormal activity or enlargement.
Iodine-131 Whole Body Scan:
Employs radioactive iodine to detect residual thyroid tissue and metastases, particularly in thyroid cancer.
Iodine-131 MIBG Scan:
Uses a specialized tracer for evaluating neuroendocrine tumors and related conditions.
Bone Scan (MDP) Whole Body:
A comprehensive skeletal assessment that identifies bone abnormalities, including metastases.
Tc 99m Whole Body Scan:
A versatile imaging modality for evaluating multiple organ systems and detecting various pathologies.
Thyroid Scan
RNM Services

In-house Radiotracer Preparation
Safe and Minimal Injection

Targeted Organ Uptake

Advanced Imaging Technique
Lodine-131 Whole Body Scan
MIBG Scan
Scintimammography


